Thyroid disorders are conditions that affect the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland in the front of the neck. The thyroid has important roles to regulate numerous metabolic processes throughout the body. Different types of thyroid disorders affect either its structure or function.
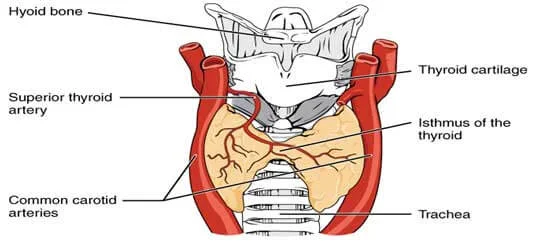
The thyroid gland is located below the Adam's apple wrapped around the trachea (windpipe). A thin area of tissue in the gland's middle, known as the isthmus, joins the two thyroid lobes on each side. The thyroid uses iodine to produce vital hormones. Thyroxine, also known as T4, is the primary hormone produced by the gland. After delivery via the bloodstream to the body's tissues, a small portion of the T4 released from the gland is converted to triiodothyronine (T3), which is the most active hormone.
The function of the thyroid gland is regulated by a feedback mechanism involving the brain. When thyroid hormone levels are low, the hypothalamus in the brain produces a hormone known as thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) that causes the pituitary gland(located at the base of the brain) to release thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to release more T4.
Since the thyroid gland is controlled by the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, disorders of these tissues can also affect thyroid function and cause thyroid problems.
Just as the types of thyroid conditions can vary, so can the symptoms of thyroid problems. Here, we have listed ten common symptoms of thyroid disease
1. Nervousness and tremor: These symptoms, along with agitation, can signal an overfunction of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism).
2. Mental fogginess and poor concentration:Mental functioning can be affected in both hyperthyroidism (elevated levels of thyroid hormone) and hypothyroidism (too low levels of thyroid hormones). While sluggishness anddepressed mood are often associated with hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism can also lead to a reduced capacity for concentration.
3. Menstrual changes: Hypothyroidism is sometimes associated with excessive or prolonged menstrual bleeding, while hyperthyroidism can be characterized by scanty or reduced menstrual flow.
4. Feeling bloated: Fluid retention is often a sign of an underactive thyroid gland.
5. Racing heartbeat: An increased heart rate (tachycardia) and palpitations can be symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
6. Aches and pains: Muscle aches and pain can accompany different types of thyroid problems.
7. Weight gain: A modest amount of weight gainoften accompanies conditions in which thyroid gland activity is lower than normal.
8. High cholesterol levels: An increase in blood cholesterol levels can occur in individuals with hypothyroidism.
9. Heat intolerance: People with an overactive thyroid gland often complain of intolerance to higher temperatures.
9. Heat intolerance: People with an overactive thyroid gland often complain of intolerance to higher temperatures.
It is important to remember that none of these symptoms is absolutely specific for thyroid disease. All of them may be caused by a number of different conditions and normal states. Your health care professional can order laboratory tests to evaluate the function of your thyroid gland if you have troubling symptoms.
There are specific kinds of thyroid disorders that includes:
Hyperthyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Goiter
Thyroid nodules
Thyroid cancer
An underactive thyroid, also known as hypothyroidism, is typified by decreased availability of thyroid hormones resulting in an overall slowing of bodily function.
The condition can be caused poor thyroid hormone production, reduced conversion of inactive thyroid hormone (T4) into the active form (T3), inhibited hormone receptivity, nutritional deficiencies, and other factors. Conditions such as diabetes, insulin resistance, depression, and chronic conditions can also contribute to thyroid disease.
A decrease in thyroid function caused by hypothyroidism brings with it many symptoms, including:
Sensitivity to cold temperatures
Difficulty losing weight
Weight gain
Muscle and joint pain or weakness
Depression
Fatigue
Difficulty thinking clearly
Brittle hair and nails
Thinning hair
Low libido
Infertility
PMS
In contrast to hypothyroidism, an overactive thyroid is known as hyperthyroidism. Increased thyroid production results in a hastening of your metabolism and other bodily functions. As the amount of thyroid hormone in the form of both T4 and T3 increases, the body becomes hyperactive causing patients to suffer from jitteriness, aggressive and ineffective nutrient consumption, and dangerous energy crashes.
Contributing factors of hyperthyroidism include thyroid nodules, thyroiditis, Plummer’s disease, over-conversion of T4 to T3, liver dysfunction, nutrient deficiencies, heavy metal toxicity, and others. The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is an autoimmune condition known as Graves’ disease.
As thyroid activity continues to increase, the body can suffer from a variety of different symptoms, including:
Anxiety and/or panic attacks
Inability to gain weight
Sudden weight loss
Excessive sweating
Irregular or total loss of menstruation
Insomnia
Heart palpitations
Shortness of breath
Easily triggered reflexes or jumpiness
Fluctuating highs and lows in energy level
Six to eight month’s treatment with our Unani Herbal Medicines without any side effect and 100% natural.
The HOO-IMM PLUS (A, B, C, D, E) is an absolutely new, novel, pioneering and revolutionary concept from Unani Herbal to medical science. It is a very safe, efficacious Indian medicine for the relief of AIDS according to the degree & stage of affliction.
View More