Issue :- 9
What is diabetes?

Diabetes is a serious complex condition which can affect the entire body. It is described as a ‘chronic’ condition, meaning that it lasts a long time, often for someone’s whole life. Diabetes requires daily self care and if complications develop, quality of life is reduced. There are different types of diabetes; all types are complex and serious. The three main types of diabetes are type 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes.
- Type 1 – where the pancreas doesn't produce any insulin
- Type 2 – where the pancreas doesn't produce enough insulin or the body’s cells don't react to insulin
- Another type of diabetes is gestational diabetes, occurs in some pregnant women and tends to disappear following birth.
How does diabetes affect the body?
When someone has diabetes, their body can’t maintain healthy levels of glucose in the blood. Glucose is a form of sugar which is the main source of energy for our bodies. Unhealthy levels of glucose in the blood can lead to long term and short term health complications.
For our bodies to work properly we need to convert glucose (sugar) from food into energy. A hormone called insulin is essential for the conversion of glucose into energy. In people with diabetes, insulin is no longer produced or not produced in sufficient amounts by the body. When people with diabetes eat glucose, which is in foods such as breads, cereals, fruit and starchy vegetables, legumes, milk, yoghurt and sweets, it can’t be converted into energy.
Instead of being turned into energy the glucose stays in the blood resulting in high blood glucose levels. After eating, the glucose is carried around your body in your blood. Your blood glucose level is called glycaemia. Blood glucose levels can be monitored and managed through self care and treatment.
Three things you need to know about diabetes:
- It is not one condition- there are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes
- All types of diabetes are complex and require daily care and management
- Diabetes does not discriminate, anyone can develop diabetes
Insulin is a hormone; a chemical messenger produced in one part of the body to have an action on another. It is a protein responsible for regulating blood glucose levels as part of metabolism.
Insulin has two modes of action on the body - an excitatory one and an inhibitory one:
- Insulin stimulates glucose uptake and lipid synthesis
- It inhibits the breakdown of lipids, proteins and glycogen, and inhibits the glucose pathway (gluconeogenesis) and production of ketone bodies (ketogenesis).
What is the pancreas?
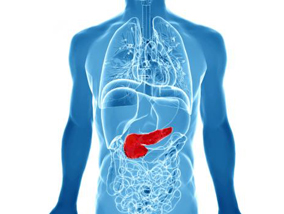
The pancreas is the organ responsible for controlling sugar levels. It is part of the digestive system and located in the abdomen, behind the stomach and next to the duodenum - the first part of the small intestine. The pancreas has two main functional components:
- Exocrine cells - cells that release digestive enzymes into the gut via the pancreatic duct
- The endocrine pancreas - islands of cells known as the islets of Langerhans within the "sea" of exocrine tissue; islets release hormones such as insulin and glucagon into
Diabetes is serious:
Diabetes can be managed well but the potential complications are the same for type 1 and type 2 diabetes including heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, limb amputation, depression, anxiety and blindness.
We know diabetes:
- Is the leading cause of blindness in working age adults
- Is a leading cause of kidney failure and dialysis
- Increases the risk of heart attacks and stroke by up to 4 times
- Is a major cause of limb amputations
- Affects mental health as well as physical health. Depression, anxiety and distress.Early diagnosis, optimal treatment and effective ongoing support and management reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Why is diabetes increasing?
All types of diabetes are increasing in prevalence:
- Type 1 diabetes accounts for 10% of all diabetes and is increasing
- Type 2 diabetes accounts for 85% of all diabetes and is increasing
- Gestational diabetes in pregnancy is increasing
Type 2 diabetes is increasing at the fastest rate. There are large numbers of people with silent, undiagnosed type 2 diabetes which may be damaging their bodies. Type 2 diabetes is one of the major consequences of the obesity epidemic. The combination of massive changes to diet and the food supply, combined with massive changes to physical activity with more sedentary work and less activity, means most populations are seeing more type 2 diabetes.
Genes also play a part with higher risk of type 2 diabetes in Chinese, South Asian, Indian, Pacific Islander and Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander populations.
Symptoms:
In type 1 diabetes, symptoms are often sudden and can be life-threatening; therefore it is usually diagnosed quite quickly. In type 2 diabetes, many people have no symptoms at all, while other signs can go unnoticed being seen as part of ‘getting older’. Therefore, by the time symptoms are noticed, complications of diabetes may already be present.
Common symptoms include:
- Being more thirsty than usual
- Passing more urine
- Feeling tired and lethargic
- Always feeling hungry
- Having cuts that heal slowly
- Itching, skin infections
- Blurred vision
- Unexplained weight loss (type 1)
- Gradually putting on weight (type 2)
- Mood swings
- Headaches
- Feeling dizzy
- Leg cramps
Unani Treatment for Insulin and non- Insulin patients. Unani medicines are side-effects free ------
We have 3-4 drug combinations for Diabetes patient, efficacious for Diabetes and its associated
complications such as frequent urination, itching, fatigue, sexual weakness etc, gangrene,
prophylactic treatment for hereditary diabetes.
The 4 drug combinations and its actions are:-
1) HOODIAB (A) - Decreases Triglyceride in the patient thus safeguards from Heart related problems and High BP.
2) HOODIAB (B)- Increases the Serum Insulin in the patient thus brings the glycosylated hemoglobin in the excellent range of 6-7 % thus decreases the Blood Sugar level to normal range.
3) HOODIAB (C)- Enhance the functions of liver and kidney. Restores the Sexual Debility and enormously enhance the sexual vigor and vitality in Diabetic patients.
4) HOODIAB (D)- Meant only for the patient undergoing the Insulin injection.
Actions of the drugs in totality:
1) Effective galactagogue, leads to pituitary or hypothalamus activity.
2) Bitters, stimulates gently endocrine glands thus effective in lowering blood sugar.
3) Raise levels of glucose and ATP in the cell, thus maintain energy levels.
4) Decreasing the consumption of insulin, thus of potential use in diabetic angioplasty, especially as it has minimal impact on glucose metabolism, making it appropriate for diabetics, who generally suffer from insufficient circulation.
5) Restores energy and vitality and ward off tiredness & fatigue ness due to sexual weakness.
6) Prophylactic, works to avoid the various long-term complications.
7) Heart and vascular tonics, appropriate for long-term use. You can evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment by undergoing the current blood test pertaining to the below mentioned test and repeating it after every month.
1) Blood Testing both Fasting & PP
2) Serum Insulin for PP, in order to know the metabolism
3) Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)
4) Lipid Profile
Feel free to write to us for any further queries.
Yours Truly,
Dr.(Hakim) Aslam Javed
draslamjaved67@gmail.com
0091-9891759909
0091-9910201126
Copyright 2014 Unani Herbal
If you wish to cancel your subscription to this newsletter click here





